Buying a home in Arizona is one of the most exciting steps you can take, whether you’re drawn to the mountain views in Scottsdale, the family neighborhoods of Gilbert and Mesa, or the desert charm of Tucson. But before you start touring homes or scrolling through listings, there’s one essential document that sets the stage for your success: your pre-approval letter.
A pre-approval letter is your proof that you’re financially ready to buy and that a lender has reviewed your information. In Arizona real estate, where homes vary from new-build communities to luxury golf-course estates, this letter helps you focus your search and make confident offers.
As an Arizona mortgage expert, I’ve seen how much smoother the process becomes once buyers get pre-approved. Here’s why your pre-approval letter matters and how to get one.

What a Pre-Approval Letter Really Means for You
A pre-approval letter is a document from your lender that verifies your income, credit, and financial readiness to buy a home. It confirms that your lender has reviewed your application and is prepared to lend you a specific amount, based on your verified financial information.
Unlike a quick online calculator or estimate, pre-approval takes your actual income, assets, credit score, and debts to determine how much you can afford to borrow. When you receive your letter, you’ll know your loan limit. That helps you focus on homes that fit your budget.
More than that, pre-approval gives you confidence. You’ll shop smarter, negotiate from a position of strength, and move faster when you find the right property. It reassures real estate agents and sellers that your financing is solid.
Pre-Approval vs. Pre-Qualification
These two terms sound similar, but they mean very different things. A pre-qualification is a quick estimate, usually based on self-reported income and credit information. It’s helpful for getting a rough idea of what you might qualify for, but it’s not verified.
A pre-approval, on the other hand, is the real deal. It’s based on actual documentation, including your pay stubs, W-2s, bank statements, and a credit review. When you’re pre-approved, your lender has confirmed that you qualify for financing within a certain range.
Think of it this way: Pre-qualification is like saying, “I think I can run a marathon.” Pre-approval is having a coach verify that you’ve trained, passed the medical check, and are ready to race. When sellers see your pre-approval letter, they know your offer is serious, and that can make all the difference when it’s time to negotiate.
Why a Pre-Approval Letter Matters in Arizona’s Market
Whether Arizona is in a seller’s market or a buyer’s market, a pre-approval is one of the most powerful tools you can have as a buyer.
In places like Phoenix, Mesa, and Chandler, homes range from brand-new developments to older properties full of character. Scottsdale is known for its luxury neighborhoods, while Gilbert and Queen Creek are favorite spots for growing families. Down south, Tucson offers a mix of university-town energy and scenic desert living, while Flagstaff and Prescott draw those looking for cooler mountain air.
No matter where you’re looking, a pre-approval letter helps you stand out as a serious buyer. It tells your agent, your seller, and even yourself that you’re ready to buy. It’s also a vital budgeting tool, helping you understand monthly payments and what price range keeps your financial comfort intact.
Today’s market rewards preparedness, not pressure. Getting pre-approved early means you’ll be ready to act with confidence when you find the home that feels right.
How to Get Pre-Approved for a Home Loan in Arizona
If you’re wondering how to get pre-approved for a home loan in Arizona, you’re not alone. Many buyers hesitate because they think it’s complicated or that they need perfect credit first. The process is actually straightforward, especially with the right guidance.
Here’s how to set yourself up for success.
Check your credit early
Before you apply, it helps to know where your credit stands. Review your credit report for errors, and avoid taking on new debt right before applying.
Gather your financial documents
You’ll need a few financial documents, such as recent pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements. If you’re self-employed, prepare business tax records and profit-and-loss statements.
Know your comfort zone
Pre-approval tells you the maximum loan you can qualify for, but that doesn’t mean you have to borrow it all. What monthly payment feels manageable for your lifestyle?
Once you’ve completed your application and your documents are verified, you’ll receive your pre-approval letter, often within a day or two. After that, you can put in offers with confidence.
Remember: Pre-approval isn’t a commitment to buy. It’s your ticket to start looking with clarity and credibility.
The Arizona Home Loan Pre-Approval Process
Every lender’s process looks a little different, but the Arizona home loan pre-approval process generally follows a few clear steps. Here’s what you can expect when you work with the Kyle Wright Team:
1. Connect with us.
Start by reaching out. We’ll talk through your goals, timeline, and what you’re looking for in a home. You can apply online through our secure portal or schedule a call, whatever works best for you.
2. Complete a loan application.
You’ll fill out a short form that covers your personal information, employment history, and financial details. It’s quick and secure.
3. Provide documentation.
We’ll request documents that verify your income and assets, such as pay stubs, W-2s, tax returns, and bank statements. If you’re self-employed, we’ll look at your business income and other sources of revenue.
4. Credit and income review.
Our team will review your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and other key factors to determine your borrowing capacity.
5. Receive your pre-approval letter.
Once everything checks out, we’ll issue your pre-approval letter outlining how much you’re qualified to borrow. This is the document your real estate agent will want to have ready when you make an offer.
At this stage, you’ll know:
- Your budget
- Your estimated monthly payment
- The type of loan program that fits you best
With our help, you can start your home search fully prepared.
The Kyle Wright Team keeps this process simple and stress-free. We use secure digital tools for fast uploads, and our team is available 24/7 if you have questions. Most clients are surprised by how quick and painless pre-approval can be when it’s done right.
Common Myths About Getting Pre-Approved
Even though having a pre-approval in hand will make your homebuying process easier and smoother, there are still a few myths that make people hesitate. Let’s clear those up.
Myth 1: “Getting pre-approved will hurt my credit.”
A pre-approval involves a credit check, but the impact is typically minimal—often just a few points. It’s well worth it for the clarity and confidence you gain.
Myth 2: “I’ll wait until I find a home to get pre-approved.”
By then it might be too late. Getting pre-approved before you start shopping means you’ll already know what you can afford. It also tells sellers that you’re qualified and serious, which is crucial if another buyer makes an offer on the same house.
Myth 3: “It’s too much hassle.”
With today’s digital tools, it’s easier than ever. Our online portal lets you upload documents securely and complete the process from your phone or laptop.
Myth 4: “I won’t qualify because of my student loans or limited savings.”
There are many loan programs available, including options with low down payments and flexible debt-to-income guidelines. The Kyle Wright Team works with buyers across a wide range of financial situations, and we’ll help you find the right path forward.
What Happens After You’re Pre-Approved
Your pre-approval letter is usually valid for 60 to 90 days. During that time, you can shop for homes confidently knowing that your finances are verified.
If your situation changes, like if you take on new debt, switch jobs, or make a large purchase, you’ll need to update your lender so your pre-approval stays current.
When you find a home you love, your lender can quickly update or reissue your letter to match the offer price. That makes your offer cleaner and stronger in the seller’s eyes.
Even if your search takes longer than expected, keeping in touch with your lender ensures that your pre-approval remains accurate. Think of it as keeping your homebuying momentum ready to go.
Why Work with the Kyle Wright Team
When it comes to the Arizona home loan pre-approval process, experience and communication make all the difference. That’s where the Kyle Wright Team stands out.
An Arizona mortgage expert, Kyle Wright brings years of local lending experience to every client relationship. Here’s what sets us apart:
- Secure online application portal: Start your pre-approval from anywhere, anytime, through our easy, encrypted digital platform.
- Local expertise: We understand Arizona’s neighborhoods, lending programs, and property types, from starter homes in Mesa to luxury estates in Scottsdale.
- Partnership with real estate professionals: We work closely with your agent to make sure your pre-approval supports your offers and helps you close quickly.
- Personalized guidance: Every buyer’s story is unique. We’ll walk you through your options and help you choose the loan that fits your lifestyle and goals.
When you work with us, you’re getting a team that’s genuinely invested in your success. We’re here to guide, explain, and celebrate each milestone with you.
Take the First Step Toward Your Arizona Home
Whether you’re dreaming of a modern condo in downtown Phoenix, a family home in Gilbert, or a retreat near Sedona, your journey begins with one simple step: getting pre-approved.
Your pre-approval letter gives you clarity, confidence, and control over your homebuying experience. It’s the key that turns your plans into action, and it helps you work smarter with your real estate agent from day one.
At the Kyle Wright Team, we make the Arizona home loan pre-approval process simple, secure, and stress-free. You can start online in minutes or connect with us directly to talk through your goals.
We’ll help you understand your options, strengthen your position as a buyer, and move toward homeownership with confidence.
Ready to get started?
Start your secure pre-approval online or call us anytime at 480-663-9277. We’re here to help.
Your Arizona home is waiting. Let’s make it happen together.

















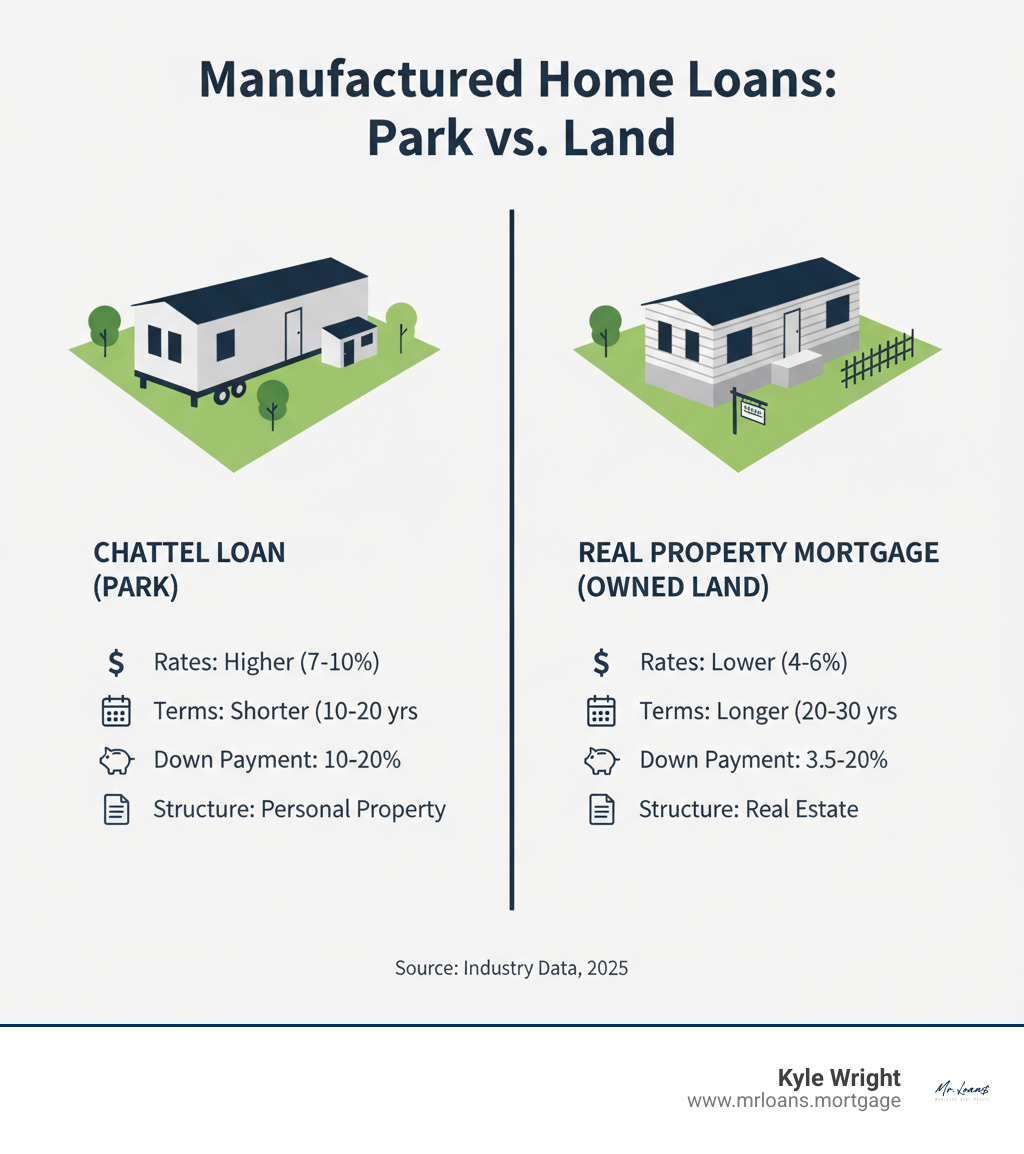


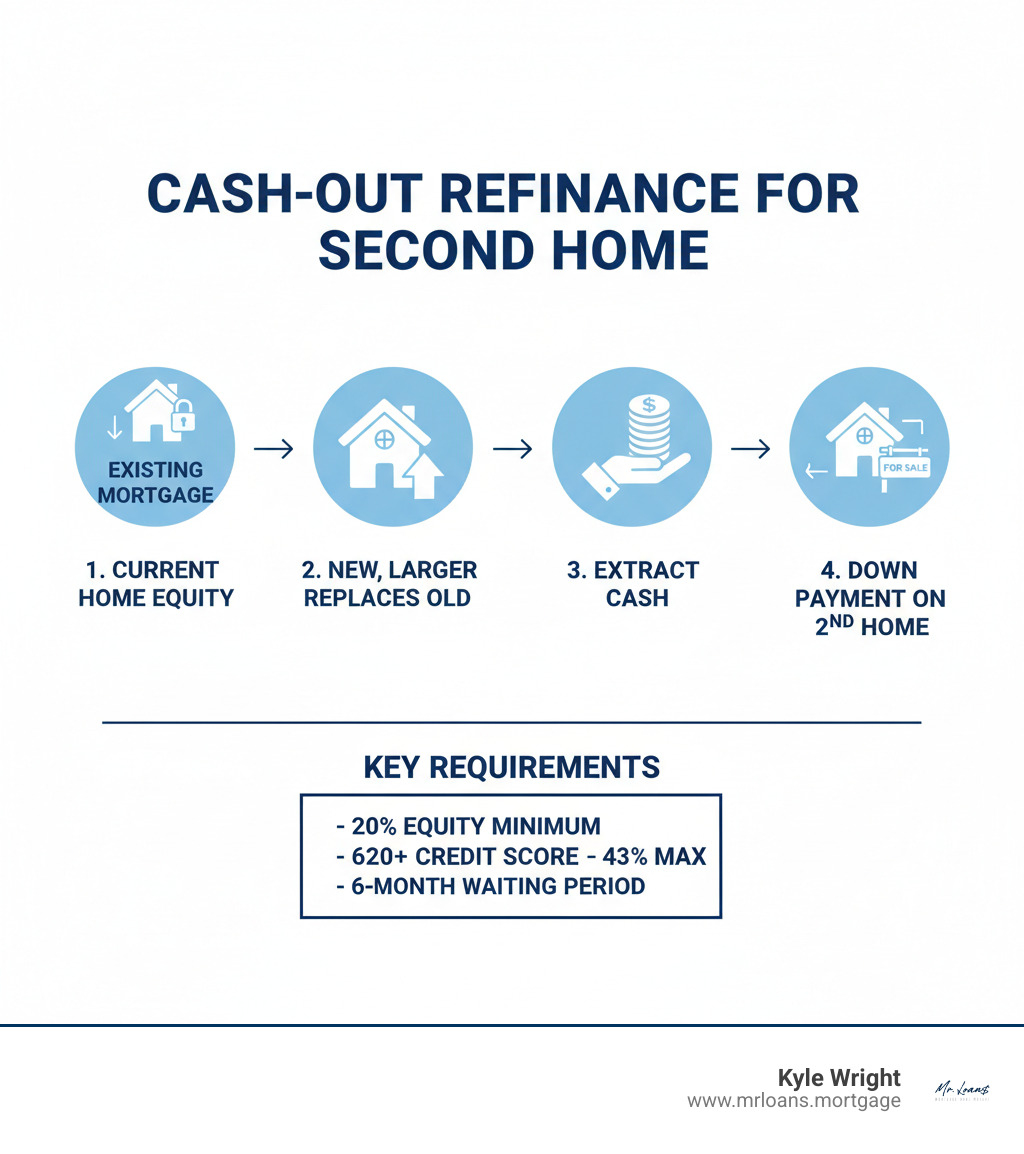


 For many homebuyers, student loans are a big part of their financial picture. The good news is that having student loan debt doesn’t automatically prevent you from getting a mortgage. Lenders look at how your student loan payments impact your overall debt-to-income ratio, rather than the total balance you owe. This means that managing your payments wisely can still make homeownership possible.
For many homebuyers, student loans are a big part of their financial picture. The good news is that having student loan debt doesn’t automatically prevent you from getting a mortgage. Lenders look at how your student loan payments impact your overall debt-to-income ratio, rather than the total balance you owe. This means that managing your payments wisely can still make homeownership possible.